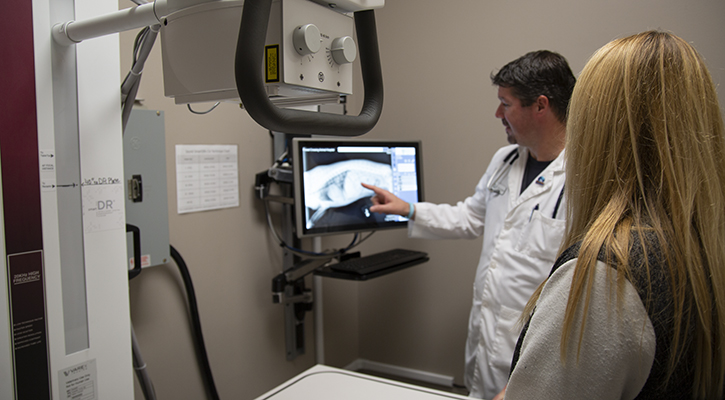
Forest Crossing Animal Hospital considers the use of digital radiograph technology as a critical tool in modern diagnostic procedures. Radiographs, which are commonly known as X-rays, are used to evaluate injuries and conditions which require more than external examination.
Radiology equipment gives us a non-evasive way to observe your pet’s internal physiology so that we can provide a more accurate diagnosis. Our veterinarians use radiographs to detect things like:
- Bone fractures
- Bladder stones
- Tumors
- Soft tissue problems (those related to the heart, stomach, intestines, reproductive, and urinary systems)
Foreign objects - And more
This pain-free process can be performed on calm and cooperative pets without sedation. However, your doctor may administer a sedative or general anesthesia in cases where a pet has trouble becoming fully relaxed.
As far as X-rays, these are evaluated on-site and during the same day by the attending doctor. In some circumstances, your pet may have to be dropped off for the day for X-rays, however we can sometimes have X-rays taken immediately to have the information needed in urgent situations. Copies of these X-rays can be digitally downloaded for pet owners at their request.
CT
We’re adding a new, state-of-the-art CT scanner to our diagnostic imaging equipment to ensure our skilled and dedicated staff can offer the best in veterinary diagnostics for your pet.
What is a CT scan?
Computerized tomography, or CT, scans are computer enhanced x-rays that provide three-dimensional images of the internal body. Unlike the two-dimensional picture an X-ray captures, CT scans allow us to see the complete structure of the body.
They are most often used to evaluate complex parts of the body, like the head, chest and various internal organs. They show different levels of tissue density, and they produce more detailed images than x-rays. This ability to see inside your pet’s body helps us detect and treat problems affecting your animal companions.
When should a CT scan be taken?
CT scans are useful in detecting problems like:
- Nasal disease
- Head trauma
- Lung diseases
- Middle and inner ear disorders
- Tumors
- Orthopedic conditions, such as hip dysplasia and joint degeneration
- Brain or spinal conditions
- Dental disease, such as abscess
